Ohm's Law,
Example Two
Determine the total resistance and potential difference between points a and b in the circuit shown. Also determine the current in, and the potential difference across, each resistor. The input current is 60 A.
Example Two
Determine the total resistance and potential difference between points a and b in the circuit shown. Also determine the current in, and the potential difference across, each resistor. The input current is 60 A.
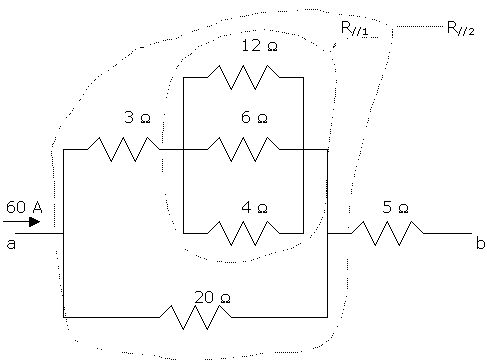
a) Total resistance between a and b.
First, calculate the 12, 6, and 4 ohm parallel combination R//1
 1/R//1 = 1/12 + 1/6 + 1/4 = 1/2. Then R//1 = 2 ohm.
1/R//1 = 1/12 + 1/6 + 1/4 = 1/2. Then R//1 = 2 ohm.
The upper branch is 3 ohms in series with R//1, 3 ohm + 2 ohm = 5 ohm.
This 5 ohm resistor is in parallel with the 20 ohm resistor, equivalent to a single resistor R//2 = 5 ohm//20 ohm:
 1/R//2 = 1/5 + 1/20 = ¼. Then R//2 = 4.
1/R//2 = 1/5 + 1/20 = ¼. Then R//2 = 4.
The total resistance between a and b is 4 ohm + 5 ohm = 9 ohms. The voltage drop or potential difference between points a and b is 60Ax9ohm = 540 V.
The total resistance between a and b is 4 ohm + 5 ohm = 9 ohms. The voltage drop or potential difference between points a and b is 60Ax9ohm = 540 V.
b) To obtain the individual currents and voltages in each resistor we can proceed as follows (there is no a unique method):
The voltage across R//2 is the difference between the total 540 voltage and the voltage drop in the 5 ohm resistor. This drop is 60Ax5ohm = 300 V. So the potential difference across R//2 is 540 V – 300 V = 240 V.
Now we can calculate the currents and voltages in the R//2combination:
In the 20 ohm resistor: current= 240 V/20 ohm = 12 A, voltage = 240 V
The upper branch has then a current of 60 A - 12 A = 48 A, or alternatively 240 V/5 ohm = 48A.
The 3 ohm resistor has a voltage of 48 Ax3 ohm = 144 V.
The R//1 combination presents a voltage of 48 AxR//1 = 48 Ax2 ohm = 96 V, or alternatively 240 V - 144 V = 96 V.
The currents in the 12 ohm, 6 ohm and 4 ohm are respectively 96/12 A=8 A, 96/6=16 A and 96/4=24 A
Now we can calculate the currents and voltages in the R//2combination:
In the 20 ohm resistor: current= 240 V/20 ohm = 12 A, voltage = 240 V
The upper branch has then a current of 60 A - 12 A = 48 A, or alternatively 240 V/5 ohm = 48A.
The 3 ohm resistor has a voltage of 48 Ax3 ohm = 144 V.
The R//1 combination presents a voltage of 48 AxR//1 = 48 Ax2 ohm = 96 V, or alternatively 240 V - 144 V = 96 V.
The currents in the 12 ohm, 6 ohm and 4 ohm are respectively 96/12 A=8 A, 96/6=16 A and 96/4=24 A
No hay comentarios.:
Publicar un comentario